Vitamin D Deficiency ICD‑10: Complete & Easy Guide
Nowadays, vitamin D deficiency is a common health issue, particularly in India. Many people have issues with absorption, diet poor, or spend less time in the sun. ICD-10 codes are used by physicians to accurately diagnose and report this condition.
This blog provides an easy-to-understand explanation of vitamin D deficiency ICD-10.
What is Vitamin-D?
Vitamin D is an important nutrient the helps our body to:
- Absorb calcium
- Keep bones and teeth strong
- Support muscle strength
- Improve immunity
Our body makes Vitamin D when sunlight falls on the skin. It is also found in some foods and supplements.
Vitamin D Deficiency ICD‑10 Code
Doctors use ICD‑10 codes for medical records and insurance purposes.
Main ICD‑10 Codes
| Condition | ICD‑10 Code |
| Vitamin D deficiency, unspecified | E55.9 |
| Vitamin D deficiency | E55 |
| Rickets due to vitamin D deficiency | E55.0 |
| Osteomalacia due to vitamin D deficiency | M83.9 |
E55.9 is the most commonly used ICD‑10 code for Vitamin D deficiency.
Why ICD‑10 Code is Important?
ICD‑10 codes help in:
- Accurate diagnosis
- Medical records
- Health insurance claims
- Research and health statistics
What is Vitamin-D Deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency happens when your body does not have enough Vitamin D to function properly.
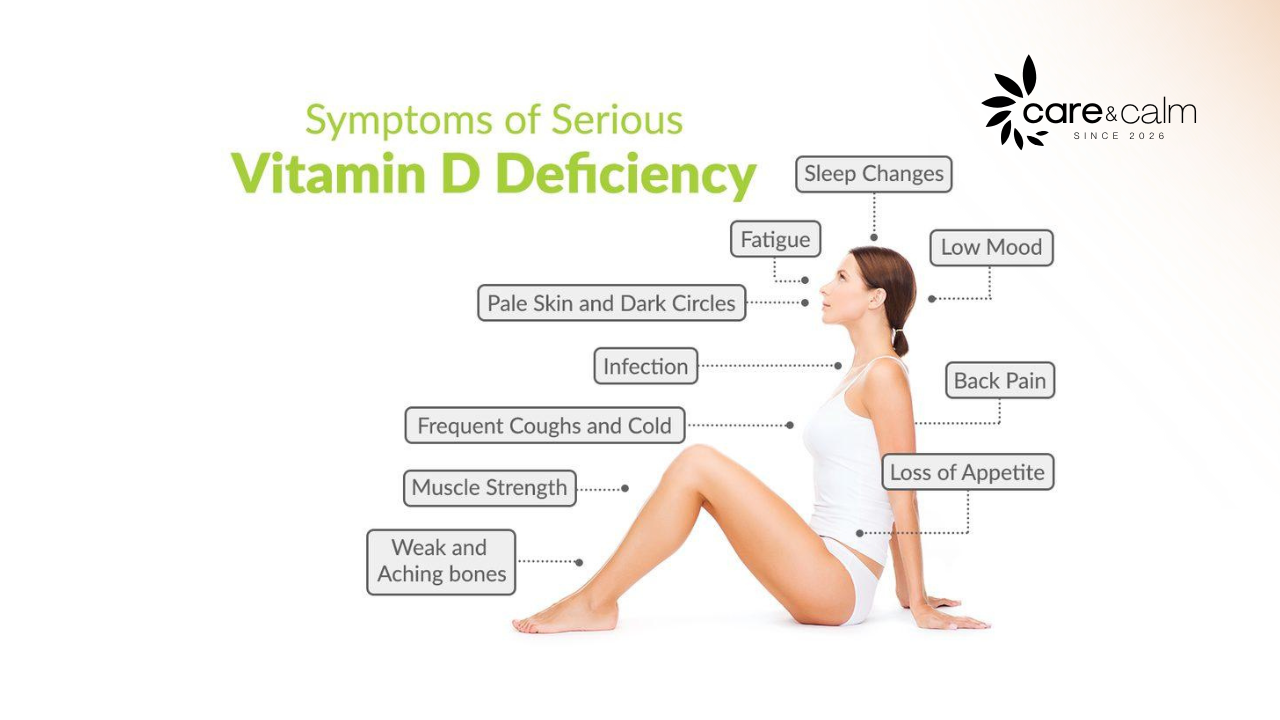
Symptoms when vitamin D Deficiency
Most people with vitamin D deficiency are asymptomatic. However, if you’re exhausted, your bones hurt, you have muscle weakness or mood changes, that’s an indication that something may be abnormal with your body.
- Fatigue
- Not sleeping well
- Bone pain or achiness
- Depression or feelings of sadness
- Hair loss
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Getting sick more easily
- Pale skin
If these symptoms sound familiar, it’s time to see a medical professional. They may do a blood test to check your vitamin D levels to see if they are within normal range.
In children, severe deficiency can cause rickets, and in adults it may lead to osteomalacia.
How is Vitamin-D deficiency Diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose Vitamin D deficiency using:
- Blood test (25‑hydroxy vitamin D test)
Normal Vitamin D Levels
- Normal: 30–100 ng/mL
- Insufficient: 20–29 ng/mL
- Deficient: Below 20 ng/mL
Tips for Vitamin D Deficiency
Treatment depends on how low your Vitamin D level is.
Common Treatment Options
- Vitamin D supplements (tablets, capsules, drops)
- Sunlight exposure (15–30 minutes daily)
- Calcium supplements (if needed)
⚠️ Always take supplements only after doctor advice.
The amount of Vitamin-D you need each day depends on your age.
The average daily recommended amounts are listed below in micrograms (mcg) and International Units (IU).
| Age / Life Stage | Recommended Amount |
| Infants up to 12 months old | 10 mcg (400 IU) |
| People 1 to 70 years old | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| Adults 71 years and older | 20 mcg (800 IU) |
| Pregnant and breastfeeding women | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
Get vitamin D from food
5 foods naturally high in vitamin D:
- Fatty fishlike salmon, trout, tuna and mackerel
- Canned fishlike herring and sardines
- Egg yolks
- Beef liver
- Fish liver
- Mushroom
- cheese
5 vitamin D fortified foods:
- Breakfast cereals
- Milk
- Almond milk
- Soy milk
- Orange juice
Since there aren’t a lot of naturally occurring vitamin D foods, many products are enriched with vitamin D. Always check the nutrition label to ensure there’s vitamin D added.
You can also read about – Austim Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Get Vitamin-D from sunlight
When your skin is exposed to ultraviolet rays from the sun, your body creates vitamin D.
Make time daily to get out in the sun. If you don’t have classes, work or commitments scheduled that require you to go outside for the day, set aside a few minutes to take a quick walk, even if it’s just around your residence hall or the block. Remember to wear sunscreen, even on cloudy, gloomy days.
If you don’t get regular sunlight, you may need to increase your dietary intake or take a vitamin D supplement.
Are vitamin D supplements safe?
Yes. A vitamin D supplement doesn’t cause many adverse effects at recommended doses. What you don’t use, your body usually urinates out, so it’s difficult to overdose on vitamin D unless you are taking massive doses.
Extremely high vitamin D levels are harmful and can cause nausea, vomiting, confusion, excessive thirst and kidney stones. Vitamin D supplements can interact with certain medications, so check with your doctor before starting one.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is Vitamin D deficiency serious?
Yes, if untreated it can cause bone problems and muscle weakness.
Can Vitamin D deficiency be cured?
Yes, with proper supplements, diet, and sunlight.
Which ICD‑10 code is used most?
E55.9 – Vitamin D deficiency, unspecified